Stephen Campbell
Jul 5, 2019
6/10
- Stefani Koorey quoting Lizzie Borden; The Preliminary Hearing in the Lizzie Borden Case (2005)
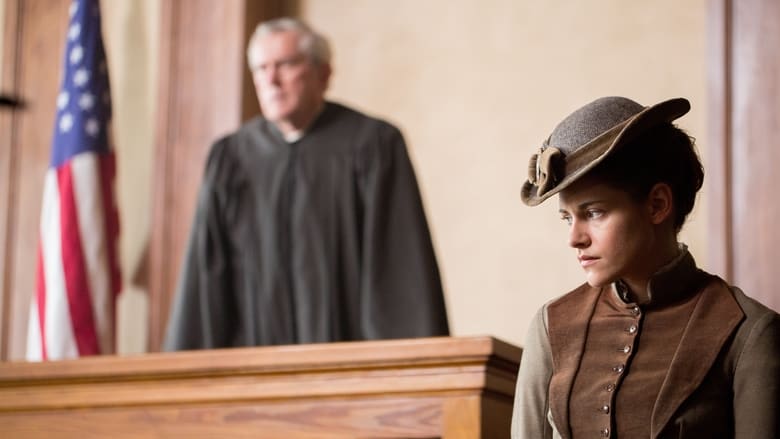
almost everything that was on the page was filmed, and a lot of it didn't make it in the movie. More stuff with me and Fiona Shaw. There was more to the relationships that made them more complicated, and also then informed why Lizzie did it. Now it's a little more vague than what Bryce and I intended.One of most interesting aspects of Lizzie is its narrative structure. Beginning on August 4 just as the (unseen) bodies are discovered, it then flashes back six months to Sullivan's arrival in the Borden house. Building up to August 4 again, this time we are shown the bodies, but we don't see the murders. It then jumps forward to the trial, before once again flashing back to August 4, this time showing us the actual killing. This pseudo-In Cold Blood structure is well-handled for the most part, and has a number of advantages. For one, it allows the film to briefly cover the trial, whilst still employing the murders as a powerful and very effective dénouement. It also allows the film to build tension around an event which the audience know is coming; by not showing the killings (twice), it has the effect that when the film does actually depict them, they are all the more impactful, placing a suitable cap on what is essentially a story of forbidden love. From an aesthetic point of view, there's much to praise, with Noah Greenberg's cinematography particularly laudable. Often framing Borden in windows, doorways, and behind railings, whilst also using shallow focus to flatten backgrounds, the sense is that this is a woman living a confined life with little room to move, trapped in her immediate environment. When she and Sullivan first kiss, the camera pulls back to reveal that Andrew is watching them – even in this moment of release, they are still trapped in his domain. Borden is also often shot off-centre, or reflected in mirrors, particularly as she talks to someone who is on camera. This reinforces the sense that she is trapped, and also feeds into the metaphorical meaning of a later scene where she spreads the shards of a broken mirror outside the door of Sullivan's room to cut her father's feet as he emerges. Dank and airless, the dimly lit Borden household, outside of which the film rarely ventures, is practically another character in and of itself. Complimenting Elizabeth J. Jones's production design, Greenberg's photography gives rise to a restrictive and claustrophobic mise en scène, which is often lit with only a single candle. However, it's not just how he lights scenes that impresses, it's also how he uses the camera; gliding over important details without hammering home why we should be paying attention (the first time we see the hatchet, for example). Also worth mentioning is how Macneill uses the full-frontal nudity towards the end of the film. Although it will no doubt be accused of gratuitousness by some, it's not only historically accurate, it's shocking, necessary, and makes a powerful statement. God forbid a woman should ever appear naked on screen in a scene not of a sexual nature. Assisting Greenberg's photography and Jones's design is Ruy García's superb sound design. Of particular note are the floorboards, which creak with the slightest touch, making any kind of clandestine interaction between Borden and Sullivan virtually impossible, and thus contributing to the sense of the household as a prison. Enhancing this even further, is the lack of warmth in the sound design, with footsteps and voices echoing and bouncing off the walls due to the lack of any soft surfaces. As a narrative of female empowerment (albeit of the homicidal variety), most of the film's main themes relate to combating the patriarchal strictures of the Gilded Age, represented primarily by Andrew and John, both loathsome characters in their own way, and Abby, who reinforces patriarchal hypocrisy by unquestioningly submitting to it (she is well aware that Andrew is abusing Sullivan, for example). Talking to the Huffington Post, Sevigny explains,
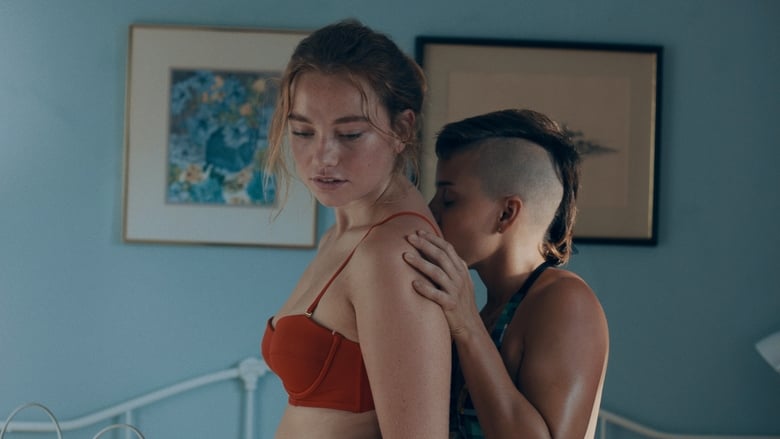
we just really wanted to focus on how she went about finding her freedom and how important that was to her and what that meant to her. Whether it was through the relationship with Bridget or ultimately killing her parents for money – because money equalled freedom then. It still does. I wanted it to be this rousing, smash-the-patriarchy piece and then she gets everything she wants, monetarily – the capitalist dream.Presenting Borden as a woman driven to her wit's end, with few practical options in a society that looks down on her because she is unwed and in her 30s, the film depicts a free-spirit living in a cage, yearning for agency, with the murders presented, at least in part, as her attempt to break free of such restrictions. Suffocated by unquestioned authoritarian patriarchal rule, Borden essentially becomes a protofeminist heroine, actively rebelling against the dominion of men and the women who enable them. Sullivan, who acts as the audience's moral compass, faces different obstacles, primarily related to economics and social caste. Her place in the ideological and socio-economic hierarchy is manifested in the fact that the family call her Maggie (the generic name given to all Irish servants). However, Borden's insistence on calling her by her actual name (which is historically inaccurate, as Borden also called her Maggie) lays the groundwork for their later emotional connection. Presenting their relationship as an illicit romance which they had to hide because of the moral bigotry of the age, the film very much adopts a #MeToo sensibility, as Borden and Sullivan fight back against self-righteous judgement, unchecked abuse, and socially sanctioned oppression. In this sense, when Borden and Sullivan strip naked before the murders, they aren't just undressing to avoid getting incriminating blood on their clothes, they are repudiating the garments that have restricted them in a physical sense just as much as men have in an ideological sense. There are, however, some sizeable problems in all of this. For one, the film lacks energy, and the slow pacing will leave some viewers bored to tears. Additionally, apart from Sevigny and Stewart, the rest of the cast is wasted, particularly Shaw, O'Hare, and Dickens (who only has a handful of scenes, and is virtually a background extra). None of their characters come across as possessing any kind of interiority, instead existing almost exclusively as archetypes; the wicked stepmother, the lecherous uncle, and the ice-cold older sister. Additionally, although he has a lot more to do, Sheridan's Andrew is completely over-the-top, only one or two beats away from a moustache-twirling mega-villain. Perhaps the most egregious problem is that the film seems as war with itself. On the one hand, it wants to be an elegant, period-appropriate tale of women attempting to take their destinies into their own hands in a Victorian society not predisposed to allow such, but on the other, it wants to present a modern story of murder and homosexual women (Patty Jenkins's Monster (2003) in corsets, if you will). At times, such as the superb depiction of the murders themselves, you can feel the modern sensibilities rise to the surface, but for the most part, they're stifled by the hushed austerity of the more muted milieu. Lizzie tells the story of an initially powerless victim who lashes out and, quite literally, slays patriarchal authority. Just by giving Sevigny the first significant starring role of her career, the film earns a lot of brownie points, as she's been an unsung, but consistently brilliant supporting player since her debut in Larry Clark's Kids (1995). Alongside her, Stewart equates herself very well, even having a decent go at an Irish accent, and the passion between the two, though period-appropriately muted, is completely believable. However, the film's attempts to shoehorn in 21st century moral values doesn't entirely work, primarily because Kass's script tips the scale in Borden's favour to a ridiculous degree – there's Andrew's over-the-top villainy (not just an authoritarian homophobe, but a rapist to boot), John's creepy intimations, Abby's refusal to stand up for her step-daughters, Borden's protofeminist rhetoric and humanitarianism, the alterations to historical fact to ensure the audience is never in any doubt as to where its sympathies are supposed to lie. Weighing the scales so decisively drains the film of any ambiguity and most of its vitality, presenting a binary story of righteous good slaying hypocritical evil, rather than a murder with many facets. A Gothic tale told from a #MeToo perspective, Lizzie tries to be many things at once – a revisionist history, a feminist tract, a championing of homosexuality, a murder mystery, a period drama – but ends up kind of falling into a no man's land between genres. Still though, there are aspects of the film that are enjoyable, if you can look past the enervating pace.